Xenophobia refers to a fear or hatred of foreigners. In this column, we will explore the meaning, types, and ways to reduce xenophobia.
Xenophobia in Our Daily Lives
On October 14, 2019, a racist incident during the Euro 2020 qualifier between Bulgaria and England became a major international issue!
During the match, Bulgarian fans directed racist chants and gestures at England's Black players, leading to the game being stopped twice. Black players like Raheem Sterling and Tyrone Mings were subjected to monkey chants and Hitler salutes.
This incident caused a huge uproar in the international community. The Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) fined the Bulgarian Football Union €85,000 and ordered one match to be played behind closed doors. Eventually, the president of the Bulgarian Football Union and the national team coach resigned.
(Source: Scroll.in)
―
What is Xenophobia?
―
A. Xenophobia comes from the Greek words 'xenos' (stranger) and 'phobos' (fear), meaning a fear or hatred of foreigners. More precisely, it refers to an irrational fear, hatred, or rejection of people from other countries or with different cultural backgrounds.
In other words, xenophobia is the phenomenon of hating and despising people from different cultural backgrounds.
"The unreasonable fear or hatred of foreigners or people from different nationalities or ethnicities."
— United Nations —
The European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights (FRA) includes xenophobia under the broader category of hate crimes, addressing it in terms of race, ethnicity, religion, and sexual orientation.
Xenophobia can also be linked to nationalism, racism, and socioeconomic factors. Examples include anti-Semitism in European societies, White Australia policy, and Islamophobia in the US and Europe.
Xenophobia appears in various forms around the world and has become increasingly severe in recent years.
∎ Increasing Xenophobia in Europe
According to a report by the European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights (FRA), approximately 4,000 hate crimes related to xenophobia occurred in Europe in 2019 alone. These crimes stemmed from discrimination and prejudice based on race, ethnicity, and religious background.
∎ Rising Xenophobia During the COVID-19 Pandemic
The International Organization for Migration (IOM) reported that xenophobia surged in many countries during the COVID-19 pandemic. Hatred towards Asians was particularly prominent, leading to violent incidents in some areas.
Xenophobia is thus a serious global issue that requires international cooperation and response to resolve.
―
What Types of Xenophobia Exist?
―
Major international organizations classify xenophobia as follows:
∎ Racial and Ethnic Xenophobia
• Irrational fear or hatred of specific races or ethnicities.
• Examples: Discrimination and hatred towards African, Asian, and Latin American ethnicities.
∎ Cultural Xenophobia
• Fear or hatred of people with different cultural backgrounds.
• Examples: Conflicts and hatred arising from differences in language, customs, and religious beliefs.
∎ Religious Xenophobia
• Discrimination and hatred towards people of specific religions.
• Examples: Hatred towards Muslims, Jews, Hindus, etc.
∎ Economic Xenophobia
• Fear and hatred stemming from the perception that foreign workers are taking away jobs.
• Examples: Excessive fear of the impact of immigrants on the domestic labor market.
∎ Political Xenophobia
• Prejudice and hatred towards people from specific countries or political systems.
• Examples: Hatred based on political ideology due to nationality.
―
Why is Xenophobia a Critical Issue?
―
Racism leads to violence, migration, and inequality, affecting not only individuals but also society, nations, and the world at large.
Xenophobia has the following consequences:
1. Violation of Human Rights
Xenophobia causes significant physical and mental harm to many people, reducing their quality of life and leading to social exclusion.
2. Economic Loss
Foreign workers and immigrants play crucial roles in many countries' economies. If they are unable to work properly, it results in significant economic losses.
3. Social Conflict
Xenophobia amplifies social conflicts, divides communities, and erodes trust among people, potentially leading to violence and long-term instability.
4. Negative Impact on International Relations
Xenophobia hinders cooperation on global issues like refugee crises and pandemics, making international collaboration difficult.
―
How Can We Reduce Xenophobia?
―
What steps can we take towards an ideal world community without xenophobia?
At the World Conference against Racism, Racial Discrimination, Xenophobia and Related Intolerance held in Durban, South Africa in 2001, the Durban Declaration was adopted.
This declaration outlines key actions to eliminate racism, racial discrimination, xenophobia, and related intolerance globally:
1. Elimination of Racial Discrimination
● The declaration proposes concrete action plans, including legal reforms, education programs, and public campaigns.
2. Response to Intolerance
● Emphasizes the roles of governments and international organizations in reducing intolerance related to xenophobia through policy improvements, legal protections, and victim support.
3. Education and Awareness
● Highlights the importance of education and raising awareness to eliminate racism and xenophobia, incorporating human rights education in school curricula, and using mass media to address discrimination.
4. Protection of Minority Rights
● Recognizes the discrimination faced by racial, ethnic, and religious minorities and proposes specific measures for their protection, including legal safeguards, economic support, and social integration programs.
5. Strengthening International Mechanisms
● Stresses the need to reinforce international mechanisms to address racism and xenophobia, enhancing the roles of international human rights organizations and promoting global cooperation.
―
Which Country Has the Least Xenophobia?
―
Which country has the least xenophobia?
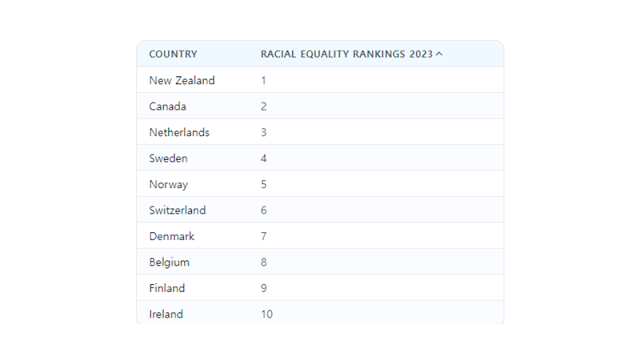
World Population Review annually announces the global racial equality rankings based on the World Values Survey and US News & World Report.
In 2023, the ten countries with the least racial discrimination were: New Zealand, Canada, Netherlands, Sweden, Norway, Switzerland, Denmark, Belgium, Finland, and Ireland.
These countries excel in education to reduce racism and xenophobia, legal protections for foreigners, and support for victims.
2023's Top 10 Countries with the Least Racial Discrimination
(Source: World Population Review)
―
Embrace Diversity as Enrichment!
―
In Thomas More's 'Utopia,' an ideal society on a fictional island is depicted where religious and cultural diversity is embraced, leading to communal prosperity.
In these times when the world feels more divided than ever, the 'tolerance' of Utopia is desperately needed.
We all become foreigners at some point. In an era of free border crossings, what we truly need to overcome is a narrow mindset.
UN Secretary-General António Guterres emphasized, “Recognizing diversity as enrichment and fighting against racism is a concrete struggle needed in all societies.”
Let’s strive to see diversity as enrichment rather than a difference. If everyone feels respected as valuable members of society, many social problems will be solved.
“Racism begets violence, displacement, and inequity. It lives on because we allow it to. It penetrates society because we fail to acknowledge diversity”
-Antonio Guterres,Secretary general of the United Nations-
|
Learn more
European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights |
Written by: Director Choi Yeon-jae